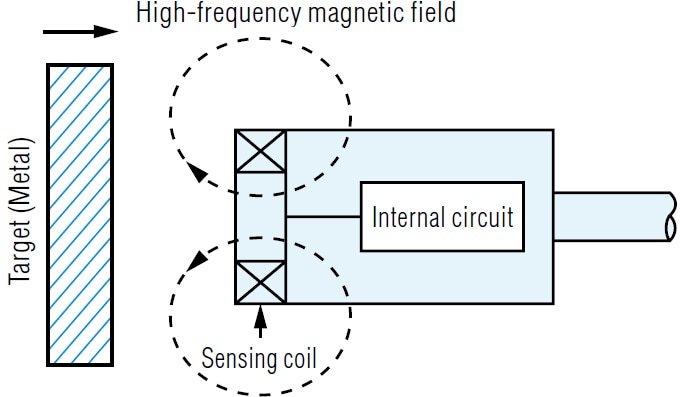
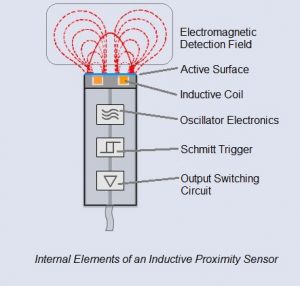
Detection principle of inductive proximity sensors inductive proximity sensors detect magnetic loss due to eddy currents that are generated on a conductive surface by an external magnetic field.
Magnetic proximity switch working principle.
These proximity switches have the disadvantage of being more sensitive to objects that conduct electricity than to objects that do not.
Magnetic proximity sensors are actuated by the presence of a permanent magnet.
Magnetic proxes are also used in clean in place cip systems at diverter panels to detect the position of the diverter pipe through the panel faceplates typically made of stainless steel.
Strong magnetic fields can cause standard inductive proximity sensors to latch on.
An ac magnetic field is generated on the detection coil and changes in the impedance due to eddy currents generated on a metallic object are detected.
Their operating principle is based on the use of reed con tacts whose thin plates are hermetically sealed in a glass bulb with inert gas.
These magnetic proximity sensors can detect the exact position of the pig from outside the wall of the stainless steel pipe.
Look for sensors designed properly by a reputable manufacturer and or look for sensors specifically designed to work at higher temperatures.
Detection through plastic wood and any non magnetisable metals.
There are several operating principles used including reed switches gmr inductive variable reluctance magneto resistive or hall effect sensors.
Inductive proximity sensors are used for non contact detection of metallic objects.
These switches sense distances to objects by generating magnetic fields.
The presence of a metallic object actuator in the operating area causes a dampening of the oscillation amplitude.
When the plate nears an object the radio frequency changes and the frequency detector sends a signal telling the switch to open or close.
Proximity sensors comprise of a permanent magnet and a pick up coil.
A radio frequency oscillator is connected to a metal plate.
The presences of a magnetic field makes the thin plates flex and touch each other causing an electrical contact.